Decoding Economic Indicators: Understanding the US Inflation Rate
In the intricate web of economic indicators, the US Inflation Rate holds a central position, influencing everything from consumer purchasing power to interest rates. This article delves into the nuances of the US inflation landscape, exploring trends, factors, and the implications that shape the economic narrative.
Understanding the US Inflation Rate
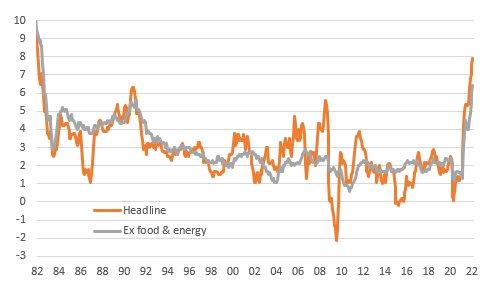
The US Inflation Rate is a measure of the average price change in a basket of goods and services over time. Tracked by indices like the Consumer Price Index (CPI) and the Producer Price Index (PPI), it provides a snapshot of the overall price movement in the economy. Understanding this metric is crucial for economists, policymakers, businesses, and consumers alike.
Factors Influencing Inflation Trends
Various factors contribute to the fluctuations in the US Inflation Rate. Demand and supply dynamics, wage levels, energy prices, and global economic conditions are among the primary influencers. Analyzing these factors helps in deciphering whether inflationary pressures are driven by increased consumer demand, supply chain disruptions, or external economic events.
Types of Inflation and Their Impact
Inflation isn’t a uniform phenomenon, and different types have different impacts. Demand-pull inflation, cost-push inflation, and built-in inflation each have distinct origins. Recognizing these types is vital for policymakers as they implement strategies to manage inflation and its effects on different sectors of the economy.
Monetary Policy and the Federal Reserve’s Role
The Federal Reserve plays a pivotal role in managing inflation through monetary policy. The central bank adjusts interest rates and implements open market operations to influence the money supply. Striking a balance between fostering economic growth and preventing excessive inflation is a delicate task that requires vigilant monitoring and strategic decisions.
Inflation’s Impact on Consumer Purchasing Power
For consumers, the impact of inflation is direct and tangible. As prices rise, the purchasing power of money decreases. Understanding how inflation affects real wages and disposable income helps individuals and households make informed financial decisions, from budgeting to investment planning.
Business Strategies Amidst Inflationary Pressures
Businesses face challenges in navigating an inflationary environment. Rising production costs, fluctuating commodity prices, and the need to adjust pricing strategies are common concerns. Crafting resilient business strategies involves anticipating inflation trends, implementing cost-saving measures, and, in some cases, passing increased costs onto consumers.
Real Estate Dynamics in Inflationary Environments
Inflation can have a significant impact on real estate markets. While property values may rise, the cost of construction materials and financing can also increase. Real estate investors and homeowners alike must consider these dynamics when making decisions about buying, selling, or investing in property.
Global Economic Interconnectedness
The US Inflation Rate is not isolated from global economic trends. International trade dynamics, commodity prices, and geopolitical events can influence inflationary pressures. Recognizing the interconnectedness of the global economy is essential for policymakers and businesses alike to navigate the complexities of inflation.
Inflation Expectations and Forward Guidance
Anticipating inflation trends is a key aspect of economic planning. Central banks often provide forward guidance on their inflation expectations, influencing market expectations. Understanding these projections is crucial for businesses, investors, and policymakers as they formulate strategies in response to expected inflationary trends.
The Path Forward: Inflation Forecasting and Economic Resilience
As the economic landscape evolves, forecasting inflation becomes a critical component of strategic planning. Proactive measures, such as diversifying investments, adjusting spending habits, and staying informed about economic indicators, contribute to individual and collective economic resilience.
In conclusion, the US Inflation Rate is a dynamic and influential economic indicator that requires continuous analysis and interpretation. Navigating its complexities involves a multidimensional approach, considering economic factors, policy decisions, and their collective impact on various stakeholders. To stay informed about the US Inflation Rate and its implications, visit US Inflation Rate for valuable insights and resources.